Delegate installation options
Install the default delegate
Expand the section below for instructions on installing the default delegate for your Harness account. It can be either a Kubernetes delegate installed using a Helm chart, Terraform Helm Provider, or Kubernetes manifest or a Docker delegate using the docker run command. For more information, go to Install Harness Delegate on Kubernetes or Docker.
Install the default delegate on Kubernetes or Docker
The Harness Delegate is a lightweight worker process that is installed on your infrastructure and communicates only via outbound HTTP/HTTPS to the Harness Platform. This enables the Harness Platform to leverage the delegate to execute the CI/CD and other tasks on your behalf, without any of your secrets leaving your network.
You can install the Harness Delegate on either Docker or Kubernetes.
You might need additional permissions to execute commands in delegate scripts and create Harness users.
Install the default Harness Delegate
Create a new delegate token
You can install delegates from the Account, Project, or Org scope. In this example, we'll create a new token in the Account scope.
To create a new delegate token, do the following:
-
In Harness, select Account Settings, then select Account Resources. The Account Resources page opens.
-
Select Delegates. The Delegates list page opens.
-
Select the Tokens tab, then select +New Token. The New Token dialog opens.
-
Enter a token name, for example
firstdeltoken. -
Select Apply. Harness generates a new token for you.
-
Select Copy to copy and store the token in a temporary file.
You will provide this token as an input parameter in the next installation step. The delegate will use this token to authenticate with the Harness Platform.
Get your Harness account ID
Along with the delegate token, you will also need to provide your Harness accountId as an input parameter during delegate installation. This accountId is present in every Harness URL. For example, in the following URL:
https://app.harness.io/ng/#/account/6_vVHzo9Qeu9fXvj-AcQCb/settings/overview
6_vVHzo9Qeu9fXvj-AcQCb is the accountId.
When you install a delegate via the Harness UI, several dependencies in this topic are prefilled for your convenience. This topic explains where to find the required information for CLI-based installation.
For more information, go to View account info and subscribe to downtime alerts.
- Kubernetes
- Docker
Prerequisite
Ensure that you have access to a Kubernetes cluster. For the purposes of this tutorial, we will use minikube.
Harness supports Kubernetes versions 1.25.16, 1.26.10, and 1.27.8 for delegate installation.
Install minikube
-
On Windows
choco install minikubeinfoFor Chocolatey installation instructions, go to Installing Chocolatey in the Chocolatey documentation.
For additional options to install minikube on Windows, go to minikube start in the minikube documentation.
-
On macOS:
brew install minikubeinfoFor Homebrew installation instructions, go to Installation in the Homebrew documentation.
Now start minikube with the following config.
minikube start --memory 4g --cpus 4
Validate that you have kubectl access to your cluster.
kubectl get pods -A
Now that you have access to a Kubernetes cluster, you can install the delegate using any of the options below.
- Helm Chart
- Terraform Helm Provider
- Kubernetes Manifest
Install the Helm chart
As a prerequisite, you must have Helm v3 installed on the machine from which you connect to your Kubernetes cluster.
You can now install the delegate using the delegate Helm chart. First, add the harness-delegate Helm chart repo to your local Helm registry.
helm repo add harness-delegate https://app.harness.io/storage/harness-download/delegate-helm-chart/
helm repo update
helm search repo harness-delegate
We will use the harness-delegate/harness-delegate-ng chart in this tutorial.
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
harness-delegate/harness-delegate-ng 1.0.8 1.16.0 A Helm chart for deploying harness-delegate
Now we are ready to install the delegate. The following example installs/upgrades firstk8sdel delegate (which is a Kubernetes workload) in the harness-delegate-ng namespace using the harness-delegate/harness-delegate-ng Helm chart.
You can install delegates from the Account, Project, or Org scope. In this example, we'll install a delegate in the Account scope.
To install a delegate, do the following:
-
In Harness, select Account Settings, then select Account Resources. The Account Resources page opens.
-
Select Delegates. The Delegates list page opens.
-
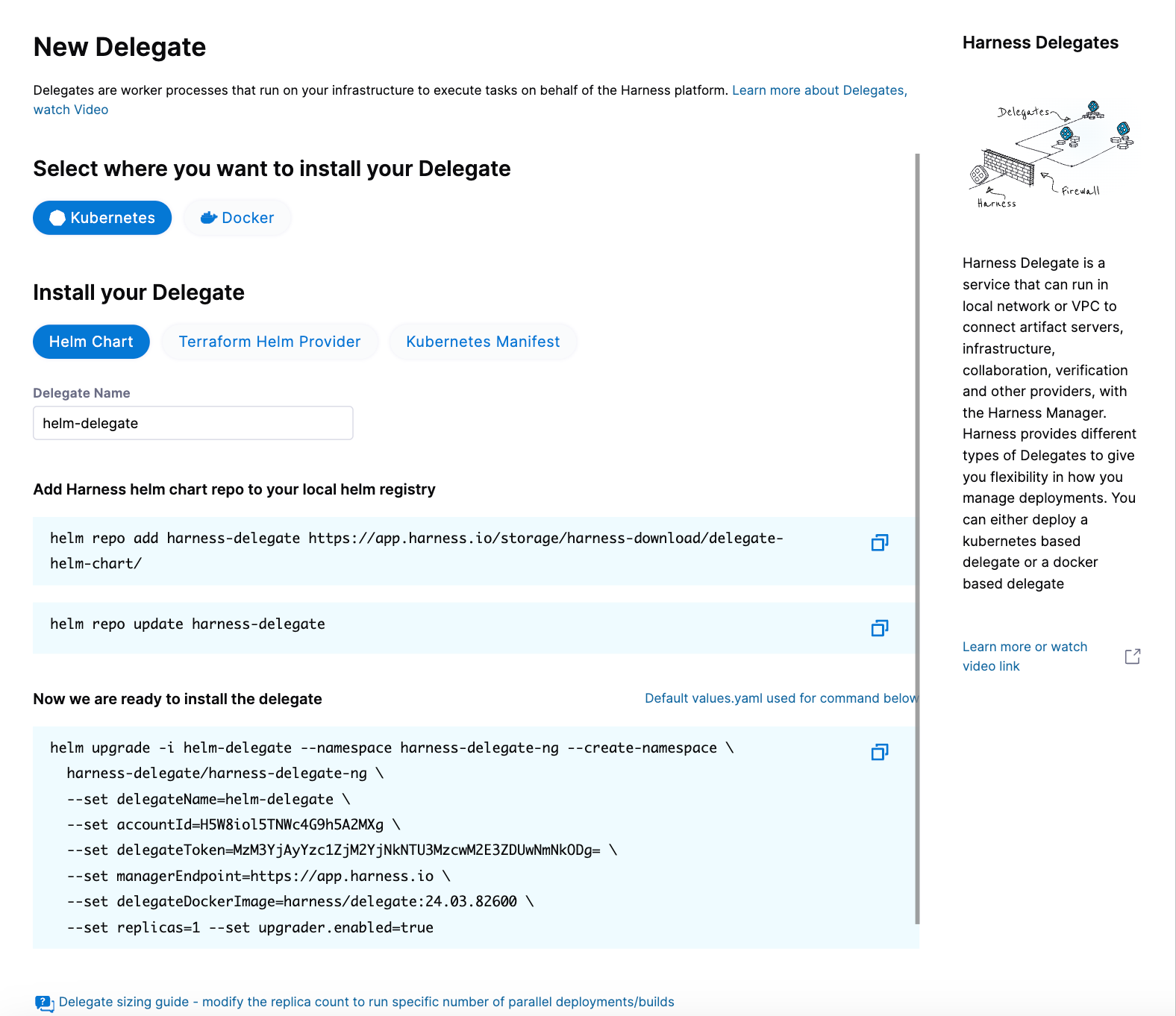
Select New Delegate. The New Delegate dialog opens.
-
Under Select where you want to install your Delegate, select Kubernetes.
-
Under Install your Delegate, select Helm Chart.
-
Copy the
helm upgradecommand.The command uses the default values.yaml file located in the delegate Helm chart GitHub repo. To make persistent changes to one or more values, you can download and update the
values.yamlfile according to your requirements. Once you have updated the file, you can use it by running the upgrade command below.helm upgrade -i firstk8sdel --namespace harness-delegate-ng --create-namespace \
harness-delegate/harness-delegate-ng \
-f values.yaml \
--set delegateName=firstk8sdel \
--set accountId=PUT_YOUR_HARNESS_ACCOUNTID_HERE \
--set delegateToken=PUT_YOUR_DELEGATE_TOKEN_HERE \
--set managerEndpoint=PUT_YOUR_MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT_HERE \
--set delegateDockerImage=harness/delegate:yy.mm.verno \
--set replicas=1 --set upgrader.enabled=true
To install a Helm delegate for Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition in an air-gapped environment, you must pass your certificate when you add the Helm repo.
helm repo add harness-delegate --ca-file <.PEM_FILE_PATH> <HELM_CHART_URL_FROM_UI>
For more information on requirements for air-gapped environments, go to Install in an air-gapped environment.
- Run the command.
Create main.tf file
Harness uses a Terraform module for the Kubernetes delegate. This module uses the standard Terraform Helm provider to install the Helm chart onto a Kubernetes cluster whose config by default is stored in the same machine at the ~/.kube/config path. Copy the following into a main.tf file stored on a machine from which you want to install your delegate.
module "delegate" {
source = "harness/harness-delegate/kubernetes"
version = "0.1.8"
account_id = "PUT_YOUR_HARNESS_ACCOUNTID_HERE"
delegate_token = "PUT_YOUR_DELEGATE_TOKEN_HERE"
delegate_name = "firstk8sdel"
deploy_mode = "Kubernetes"
namespace = "harness-delegate-ng"
manager_endpoint = "PUT_YOUR_MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT_HERE"
delegate_image = "harness/delegate:yy.mm.verno"
replicas = 1
upgrader_enabled = false
# Additional optional values to pass to the helm chart
values = yamlencode({
javaOpts: "-Xms64M"
})
}
provider "helm" {
kubernetes {
config_path = "~/.kube/config"
}
}
Now replace the variables in the file with your Harness account ID and delegate token values. Replace PUT_YOUR_MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT_HERE with the Harness Manager Endpoint noted below. For Harness SaaS accounts, you can find your Harness Cluster Location on the Account Overview page under the Account Settings section of the left navigation.
| Harness Cluster Location | Harness Manager Endpoint on Harness Cluster |
|---|---|
| SaaS prod-1 | https://app.harness.io |
| SaaS prod-2 | https://app.harness.io/gratis |
| SaaS prod-3 | https://app3.harness.io |
Run Terraform init, plan, and apply
Initialize Terraform. This downloads the Terraform Helm provider to your machine.
terraform init
Run the following step to view the changes Terraform is going to make on your behalf.
terraform plan
Finally, run this step to make Terraform install the Kubernetes delegate using the Helm provider.
terraform apply
When prompted by Terraform if you want to continue with the apply step, type yes, and then you will see output similar to the following.
helm_release.delegate: Creating...
helm_release.delegate: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
helm_release.delegate: Still creating... [20s elapsed]
helm_release.delegate: Still creating... [30s elapsed]
helm_release.delegate: Still creating... [40s elapsed]
helm_release.delegate: Still creating... [50s elapsed]
helm_release.delegate: Still creating... [1m0s elapsed]
helm_release.delegate: Creation complete after 1m0s [id=firstk8sdel]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Download a Kubernetes manifest template
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/harness/delegate-kubernetes-manifest/main/harness-delegate.yaml
Replace variables in the template
Open the harness-delegate.yaml file in a text editor and replace PUT_YOUR_DELEGATE_NAME_HERE, PUT_YOUR_HARNESS_ACCOUNTID_HERE, and PUT_YOUR_DELEGATE_TOKEN_HERE with your delegate name (for example, firstk8sdel), Harness accountId, and delegate token values, respectively.
Replace the PUT_YOUR_MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT_HERE variable with the Harness Manager Endpoint noted below. For Harness SaaS accounts, you can find your Harness Cluster Location on the Account Overview page under the Account Settings section of the left navigation.
| Harness Cluster Location | Harness Manager Endpoint on Harness Cluster |
|---|---|
| SaaS prod-1 | https://app.harness.io |
| SaaS prod-2 | https://app.harness.io/gratis |
| SaaS prod-3 | https://app3.harness.io |
Apply the Kubernetes manifest
kubectl apply -f harness-delegate.yaml
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have the Docker runtime installed on your host. If not, use one of the following options to install Docker:
Install on Docker
You can install delegates from the Account, Project, or Org scope. In this example, we'll install a delegate in the Project scope.
To install a delegate, do the following:
-
In Harness, select your project, then select Project Settings.
-
Under Project-level resources, select Delegates.
-
Select Install a Delegate to open the New Delegate dialog.
-
Under Select where you want to install your Delegate, select Docker.
-
Under Install your Delegate, enter a Delegate Name.
-
Copy the
docker runcommand.docker run --cpus=1 --memory=2g \
-e DELEGATE_NAME=docker-delegate \
-e NEXT_GEN="true" \
-e DELEGATE_TYPE="DOCKER" \
-e ACCOUNT_ID=YOUR_HARNESS_ACCOUNTID_ \
-e DELEGATE_TOKEN=YOUR_DELEGATE_TOKEN \
-e DELEGATE_TAGS="" \
-e LOG_STREAMING_SERVICE_URL=YOUR_LOG_STREAMING_SERVICE_URL/log-service/ \
-e MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT=YOUR_MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT \
harness/delegate:yy.mm.vernoinfoThe
docker runcommand doesn't allow you to select the delegate token. You can replace the token in the command with another token if required.infoSteps 6 and 7 are optional when installing a delegate using the CLI flow.
-
(Optional) Replace the
YOUR_MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT_HEREvariable with the Harness Manager Endpoint noted below. For Harness SaaS accounts, to find your Harness cluster location, select Account Settings, and then select Overview. In Account Overview, look in Account Settings. It is listed next to Harness Cluster Hosting Account.For more information, go to View account info and subscribe to downtime alerts.
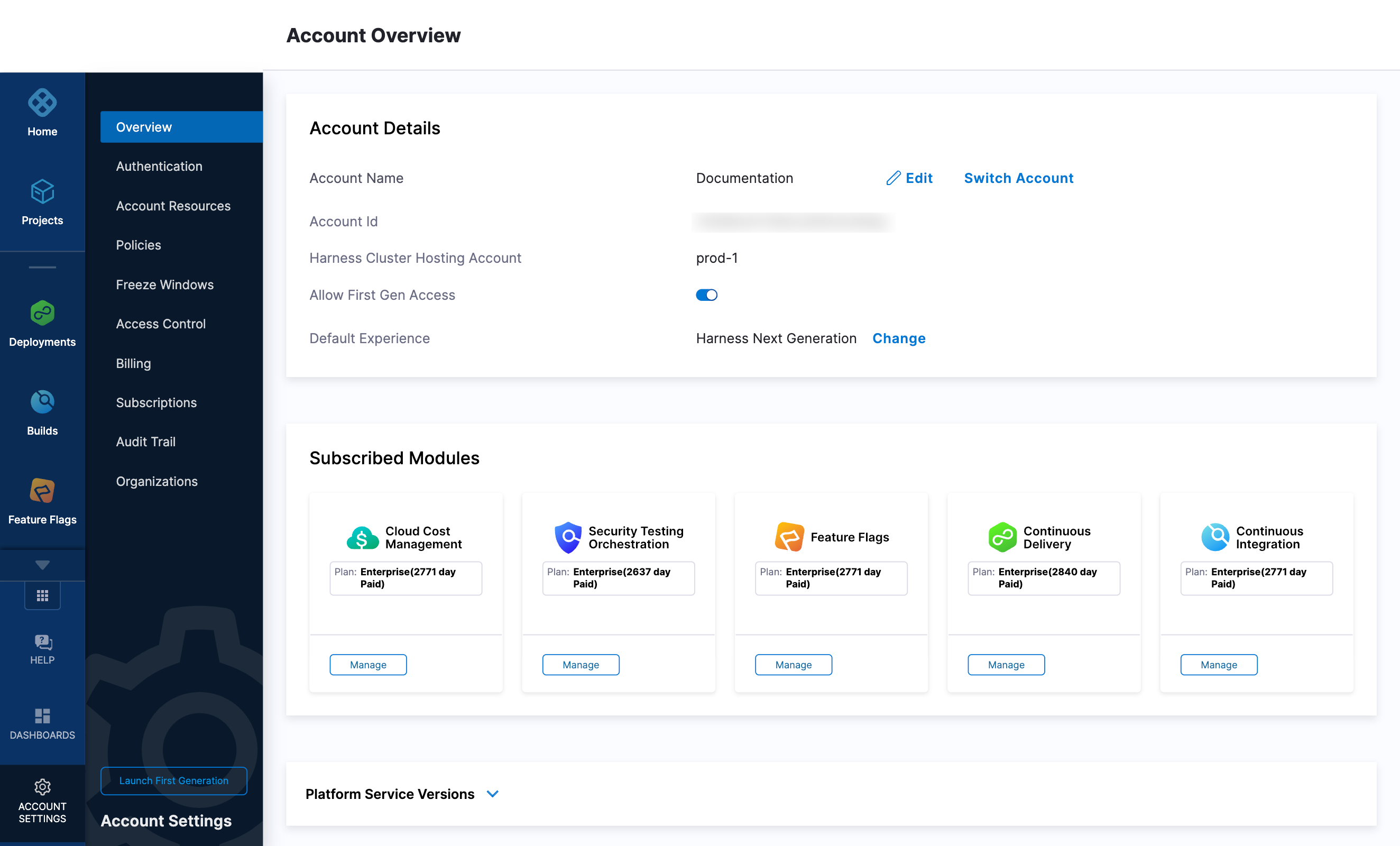
For Harness CDCE, the endpoint varies based on the Docker vs. Helm installation options.
Harness Cluster Location Harness Manager Endpoint on Harness Cluster SaaS prod-1 https://app.harness.ioSaaS prod-2 https://app.harness.io/gratisSaaS prod-3 https://app3.harness.io -
Run the command.
Deploy using a custom role
During delegate installation, you have the option to deploy using a custom role. To use a custom role, you must edit the delegate YAML file.
Harness supports the following custom roles:
cluster-admincluster-viewernamespace-admin- custom cluster roles
To deploy using a custom cluster role, do the following:
-
Open the delegate YAML file in your text editor.
-
Add the custom cluster role to the
roleReffield in the delegate YAML.---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: harness-delegate-cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---In this example, the
cluster-adminrole is defined. -
Save the delegate YAML file.
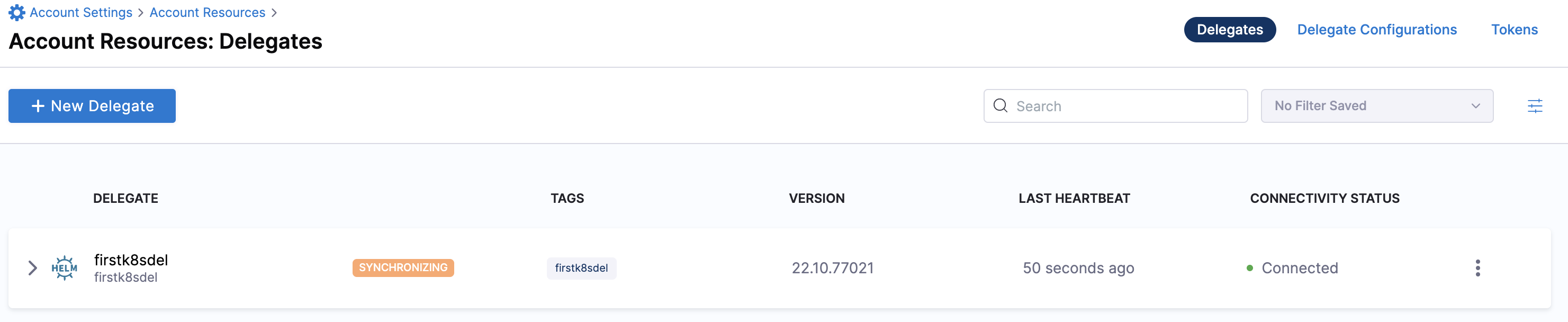
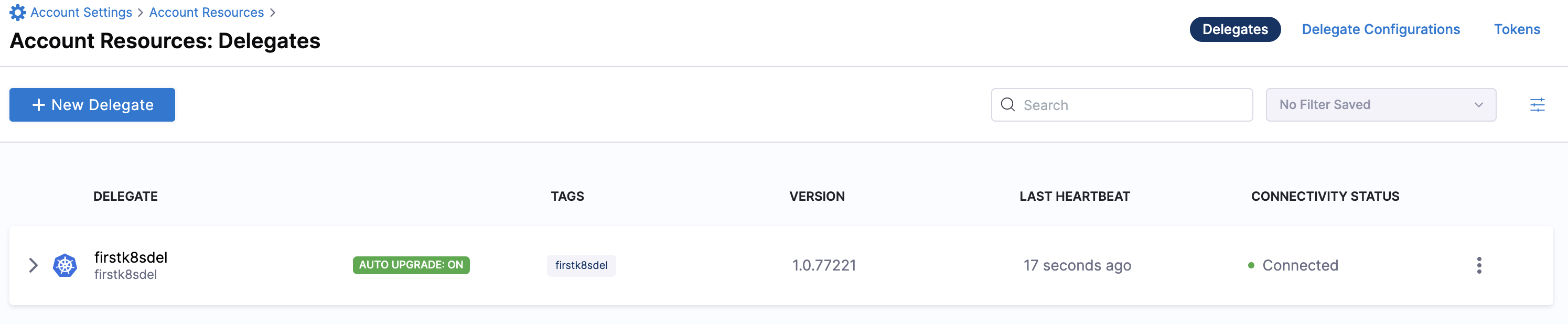
Verify delegate connectivity
Select Continue. After the health checks pass, your delegate is available for you to use. Select Done and verify your new delegate is listed.
Helm chart & Terraform Helm provider
Kubernetes manifest
Docker
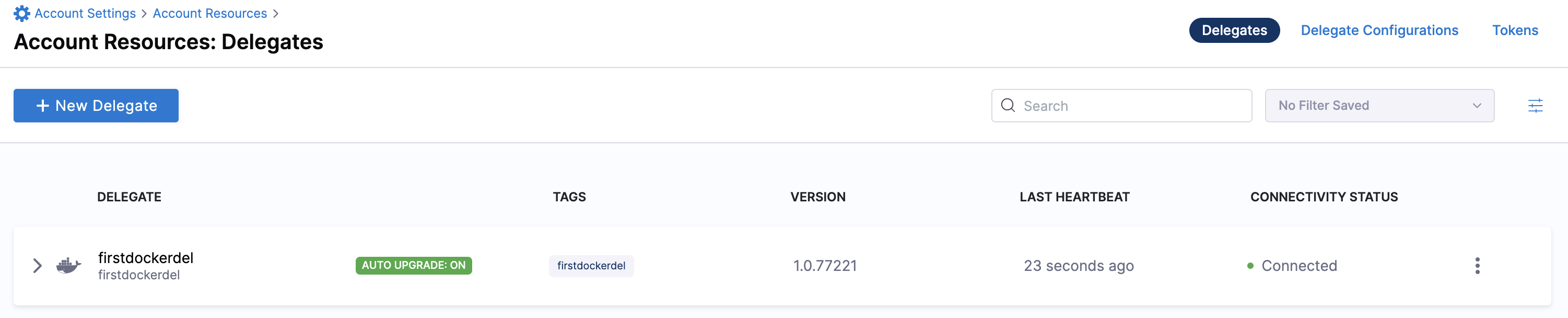
You can now route communication to external systems in Harness connectors and pipelines by selecting this delegate via a delegate selector.
Delegate selectors do not override service infrastructure connectors. Delegate selectors only determine the delegate that executes the operations of your pipeline.
Troubleshooting
The delegate installer provides troubleshooting information for each installation process. If the delegate cannot be verified, select Troubleshoot for steps you can use to resolve the problem. This section includes the same information.
Harness asks for feedback after the troubleshooting steps. You are asked, Did the delegate come up?
If the steps did not resolve the problem, select No, and use the form to describe the issue. You'll also find links to Harness Support and to Delegate docs.
- Helm Chart
- Terraform Helm Provider
- Kubernetes Manifest
- Docker
Use the following steps to troubleshoot your installation of the delegate using Helm.
-
Verify that Helm is correctly installed:
Check for Helm:
helmAnd then check for the installed version of Helm:
helm versionIf you receive the message
Error: rendered manifests contain a resource that already exists..., delete the existing namespace, and retry the Helm upgrade command to deploy the delegate.For further instructions on troubleshooting your Helm installation, go to Helm troubleshooting guide.
-
Check the status of the delegate on your cluster:
kubectl describe pods -n <NAMESPACE> -
If the pod did not start, check the delegate logs:
kubectl logs -f <DELEGATE_NAME> -n <NAMESPACE>If the state of the delegate pod is
CrashLoopBackOff, check your allocation of compute resources (CPU and memory) to the cluster. A state ofCrashLoopBackOffindicates insufficient Kubernetes cluster resources. -
If the delegate pod is not healthy, use the
kubectl describecommand to get more information:kubectl describe <POD_NAME> -n <NAMESPACE>
Use the following steps to troubleshoot your installation of the delegate using Terraform.
-
Verify that Terraform is correctly installed:
terraform -versionFor further instructions on troubleshooting your installation of Terraform, go to the Terraform troubleshooting guide.
-
Check the status of the delegate on your cluster:
kubectl describe pods -n <namespace> -
If the pod did not start, check the delegate logs:
kubectl logs -f <DELEGATE_NAME> -n <NAMESPACE>If the state of the delegate pod is
CrashLoopBackOff, check your allocation of compute resources (CPU and memory) to the cluster. A state ofCrashLoopBackOffindicates insufficient Kubernetes cluster resources. -
If the delegate pod is not healthy, use the
kubectl describecommand to get more information:kubectl describe <POD_NAME> -n <NAMESPACE>
Use the following steps to troubleshoot your installation of the delegate using Kubernetes.
-
Check the status of the delegate on your cluster:
kubectl describe pods -n <NAMESPACE> -
If the pod did not start, check the delegate logs:
kubectl logs -f <DELEGATE_NAME> -n <NAMESPACE>If the state of the delegate pod is
CrashLoopBackOff, check your allocation of compute resources (CPU and memory) to the cluster. A state ofCrashLoopBackOffindicates insufficient Kubernetes cluster resources. -
If the delegate pod is not healthy, use the
kubectl describecommand to get more information:kubectl describe <POD_NAME> -n <NAMESPACE>
Use the following steps to troubleshoot your installation of the delegate using Docker:
-
Check the status of the delegate on your cluster:
docker container ls -a -
If the pod is not running, check the delegate logs:
docker container logs <DELEGATE_NAME> -f -
Restart the delegate container. To stop the container:
docker container stop <DELEGATE_NAME>To start the container:
docker container start <DELEGATE_NAME> -
Make sure the container has sufficient CPU and memory resources. If not, remove the older containers:
docker container rm [container id]
This video shows how to install a delegate.
The default delegate image, denoted by the yy.mm.verno image tag, includes a set of pre-installed 3rd-party custom binaries for convenience. For the list of these binaries, go to Third-party tools included in the delegate image type. If you are concerned about the security vulnerabilities that potentially come with these pre-installed binaries, Harness recommends that you use the minimal delegate explained below.
Install minimal delegate with 3rd party custom binaries
The minimal delegate image, denoted by the yy.mm.verno.minimal image tag, does not include any pre-installed 3rd-party custom binaries for ensuring the lowest footprint and hence lowest number of security vulnerabilities.
Use INIT_SCRIPT
This option installs the 3rd party custom binaries on a delegate container instance without changing the delegate image. Below is an inline tutorial that shows you how to use this option. You can also review the tutorial directly. Go to Install a delegate with third-party tool custom binaries.
Use INIT_SCRIPT
The Harness Delegate is a lightweight worker process that is installed on your infrastructure and communicates only via outbound HTTP/HTTPS to the Harness Platform. This enables the Harness Platform to leverage the delegate for executing the CI/CD and other tasks on your behalf, without any of your secrets leaving your network.
The default delegates are packaged with third-party SDKs that support Kubernetes, Helm, and other Harness-integrated tools. The SDKs are included on the delegate image as binary files; depending on the tool, multiple versions are included. Harness also provides a "minimal" delegate image that doesn't include third-party SDKs.
You can modify the default and minimal Harness Delegate images. You might customize the delegate image if:
- You want to use binaries that reduce your attack surface. Vulnerability scans detect unresolved vulnerabilities in older binary versions.
- You want to use tools or versions of tools that Harness doesn't include on the default delegate image. You can install all kinds of tools, such as Git client, Helm, Terraform, PowerShell, Docker, AWS CLI, and so on.
- You need to modify where certain tools run. For example, connecting to external systems usually requires a third-party client tool or library to be present locally, and some of the Harness CD and Platform tasks require these client tools to be present in the same container instance where the delegate runs.
There are two primary ways to modify the Harness Delegate image:
- Install additional client tools along with the delegate by modifying the delegate YAML to install the tools and versions that you specify in the
INIT_SCRIPTenvironment variable. This approach works best when you are still building your CI/CD pipelines and you don't yet have the final list of required client tools. This approach is explained in this topic. - Create a custom delegate image (using the Harness-provided delegate image as a base image). This approach works best when you know all the client tools ahead of time. For instructions on building custom delegate images, go to Build custom delegate images with third-party tools.
You might need additional permissions to execute commands in delegate scripts and create Harness users.
Edit the delegate YAML
To install a delegate, you download its YAML file and run it in your target environment, such as a Kubernetes cluster. For example purposes, this topic uses a delegate installed on a Kubernetes cluster created on Google Cloud.
To modify the delegate image, you need to edit the delegate YAML file to specify delegate environment variables, the delegate base image, Harness-required SDKs (depending on the selected base image), and third-party tools to install.
You can modify the delegate YAML before or after you install the delegate. To get the delegate YAML, follow the steps to Install a delegate. To follow along with the examples in this topic, use the Kubernetes Manifest option for delegate installation.
Since the delegate is declaratively defined in YAML, it is easy to add custom scripts and customize the delegate in other ways too. SDKs and additional tools are specified in the INIT_SCRIPT, with the exception of delegate Helm chart deployments. For more examples, go to Common delegate initialization scripts.
Delegate Helm chart deployments
For delegate Helm chart deployments, add your third-party tool custom binaries to initScript in your values.yaml file to run them before delegate installation. You can find the default values.yaml file in the Delegate Helm chart GitHub repo.
For example, the following values.yaml file entry installs Kubectl on amd64 architecture. The exact install URL depends on your architecture. For additional architecture installation commands, go to the Kubernetes documentation on Installing kubectl.
# Script to run before delegate installation
initScript: "
curl -L0 https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.24.3/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl -o kubectl
chmod +x ./kubectl
mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/"
Add Harness-required SDKs
The toolset you install on the delegate minimal image must include the SDKs that Harness requires to perform tasks.
In the delegate container spec, use the INIT_SCRIPT environment variable to download the certified SDK versions that Harness requires.
The SDKs you need to add depend on the type of deployment. For a list of SDK versions certified for different deployment types, go to Delegate-required SDKs.
Example Kubernetes manifest delegate YAML with required SDK downloads
The following delegate YAML contains examples of downloads for all Harness-required SDKs. You can edit the YAML to include only the SDKs and versions Harness requires for your deployment type. To modify the export PATH, run export PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/custom-client-tools/:<path>.
...
- name: DELEGATE_TYPE
value: "KUBERNETES"
- name: DELEGATE_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: INIT_SCRIPT
value: |
## Kubectl
curl -L0 https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.24.3/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl -o kubectl
chmod +x ./kubectl
mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/
## Helm V3
curl -L0 https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.9.2-linux-amd64.tar.gz -o helm-v3.9.2.tar.gz
tar -xvzf helm-v3.9.2.tar.gz
chmod +x ./linux-amd64/helm
mv ./linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/
## Kustomize
curl -L0 https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/releases/download/kustomize%2Fv4.5.4/kustomize_v4.5.4_linux_amd64.tar.gz -o kustomize_v4.5.4.tar.gz
tar -xvzf kustomize_v4.5.4.tar.gz
chmod +x ./kustomize
mv kustomize /usr/local/bin/
## OpenShift OC
curl -L0 https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/clients/oc/latest/linux/oc.tar.gz -o oc.tar.gz
tar -xvzf oc.tar.gz
chmod +x ./oc
mv oc /usr/local/bin/
## go-template
mkdir -p /opt/harness-delegate/client-tools/go-template/v0.4.1/
curl -L0 https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/go-template/release/v0.4.1/bin/linux/amd64/go-template -o go-template
chmod +x ./go-template
mv go-template /usr/local/bin/
curl -L https://get.helm.sh/chartmuseum-v0.14.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz -o chartmuseum-v0.14.tar.gz
tar xzvf chartmuseum-v0.14.tar.gz
chmod +x ./linux-amd64/chartmuseum
mv ./linux-amd64/chartmuseum /usr/local/bin/
cd /opt/harness-delegate
...
Private Cloud Foundry (PCF) deployments
PCF deployments require CLI 7. For installation instructions, go to Install Cloud Foundry CLI versions on the Harness Delegate.
Add your custom tools
Open the delegate YAML file and locate the INIT_SCRIPT in the delegate container spec. To install additional tools on the delegate, add your custom scripts to the INIT_SCRIPT.
Several tools require unzip in the manifest. Add the following YAML before you add any of the below scripts.
- name: INIT_SCRIPT
value: |
microdnf install -y zip unzip
These examples show how to install some common tools.
- Install AWS CLI
- Install kubectl
- Install Terraform
- Install Helm
The following INIT_SCRIPT installs the AWS CLI:
- name: INIT_SCRIPT
value: |
microdnf install -y zip unzip
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip awscliv2.zip
./aws/install
The following INIT_SCRIPT installs kubectl:
- name: INIT_SCRIPT
value: |
curl -L0 https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.24.3/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl -o kubectl
chmod +x ./kubectl
mv kubectl /opt/harness-delegate/custom-client-tools/kubectl
The following INIT_SCRIPT installs Terraform:
- name: INIT_SCRIPT
value: |
microdnf install -y zip unzip
curl -O -L https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.12.25/terraform_0.12.25_linux_amd64.zip
unzip terraform_0.12.25_linux_amd64.zip
mv ./terraform /usr/bin/
The following INIT_SCRIPT installs Helm 3:
- name: INIT_SCRIPT
value: |
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh
Install Azure CLI
To install the Azure CLI, run the following.
## Install Azure CLI
rpm --import <https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc>
rpm -ivh <https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/8/packages-microsoft-prod.rpm>
microdnf install -y azure-cli
Install multiple tools at once
To install multiple tools, you can add all the install scripts to the INIT_SCRIPT, for example:
- name: INIT_SCRIPT
value: |
microdnf install -y zip unzip
## Install AWS CLI
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip awscliv2.zip
./aws/install
## Install kubectl
curl -L0 https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.24.3/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl -o kubectl
chmod +x ./kubectl
mv kubectl /opt/harness-delegate/custom-client-tools/kubectl
## Install Terraform
curl -O -L https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.12.25/terraform_0.12.25_linux_amd64.zip
unzip terraform_0.12.25_linux_amd64.zip
mv ./terraform /usr/bin/
## Install Helm3
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh
Install credentials plugin for GKE and AKS infrastructure types
Add the following install scripts to the INIT_SCRIPT to install the credentials plugin for GKE and AKS infrastructure types if you're using kubectl version 1.26.x or later.
If you're using a custom delegate with kubelogin and certificate type of authentication, then you must install Azure CLI. Alternatively, you can install the harness-credentials-plugin to take care of this flow without Azure CLI.
- name: INIT_SCRIPT
value: |
## for AKS
mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/kubelogin/v0.1.1 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/kubelogin/v0.1.1/kubelogin https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/kubelogin/release/v0.1.1/bin/linux/amd64/kubelogin
export PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/client-tools/kubelogin/v0.1.1/:$PATH
## for GKE or AKS with certificate auth type
mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/harness-credentials-plugin/v0.1.0 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/harness-credentials-plugin/v0.1.0/harness-credentials-plugin https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/harness-credentials-plugin/release/v0.1.0/bin/linux/amd64/harness-credentials-plugin
export PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/client-tools/harness-credentials-plugin/v0.1.0/:$PATH
Apply the changes
You can modify the delegate YAML before or after you install the delegate.
If you haven't yet installed the delegate, finish Installing the delegate in your target environment.
If you already installed the delegate, you need to apply the updated delegate YAML and restart the delegate. For example, if your delegate is in a Kubernetes cluster, run the kubectl command to apply it:
kubectl apply -f harness-delegate.yml
Wait a few minutes for the delegate to start up. You can check the delegate status in the Harness Platform.
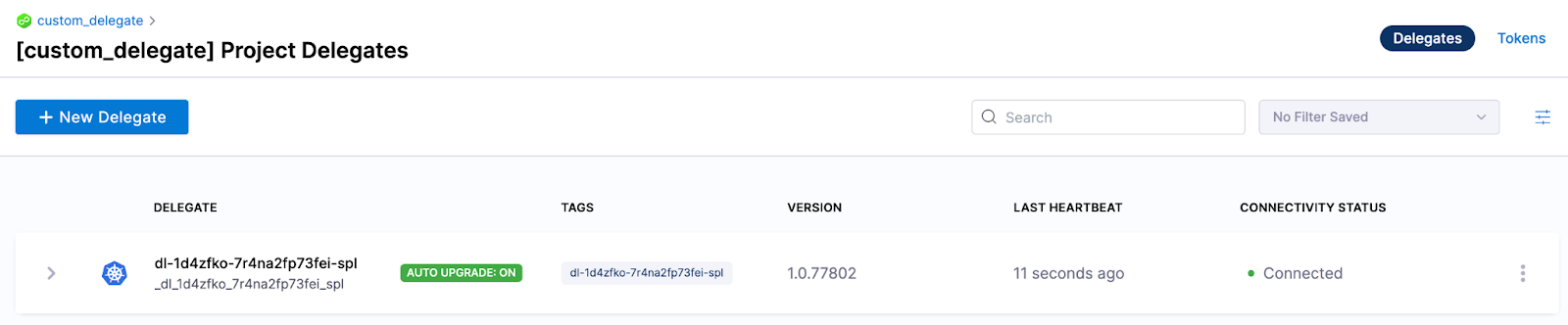
Test your tools
You can either run an existing pipeline that requires one of the tools you installed, or create a test pipeline with a simple script to confirm that a tool was installed.
-
Create a pipeline and add a Custom stage.
-
Add a Shell Script step.
-
Enter a simple script, such as a version check, for the tool that you installed.
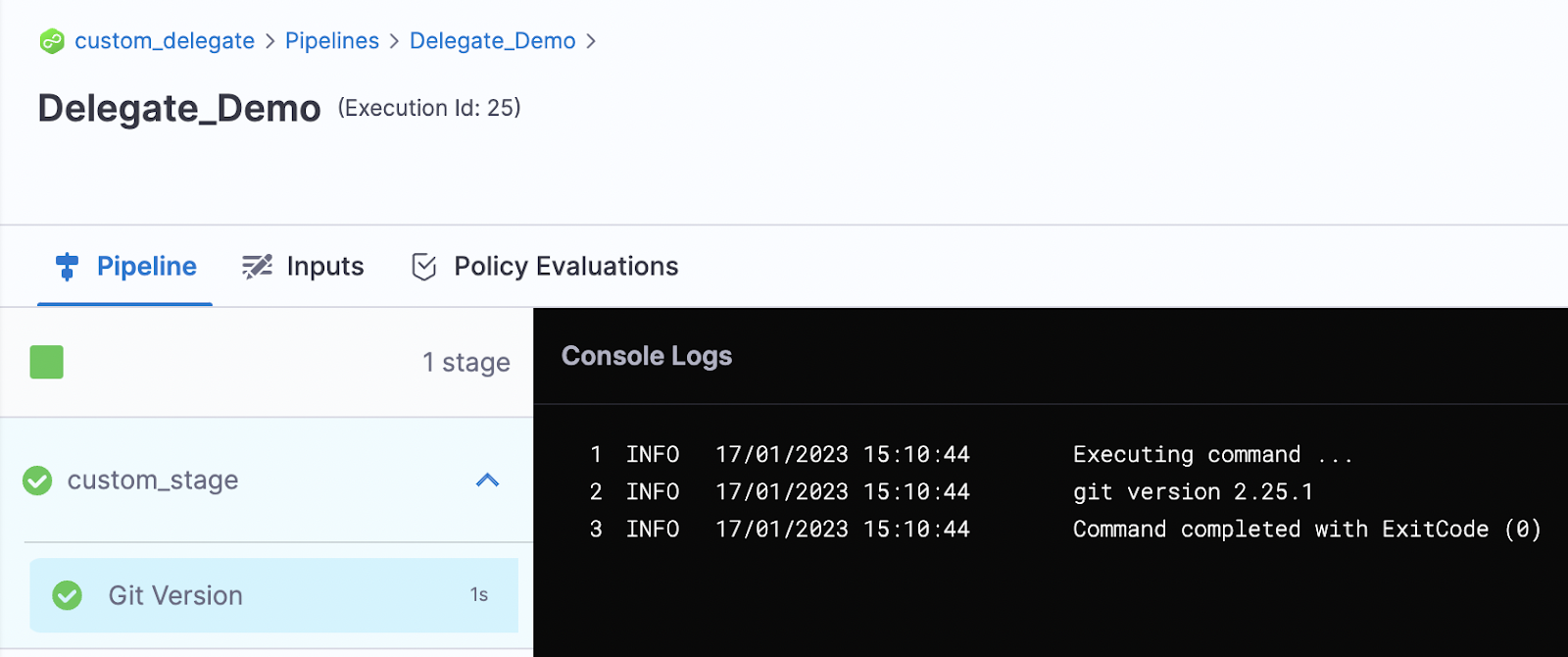
For example, if you installed the Git client, you could run
git --version, or if you installed the AWS CLI, you could runaws --version.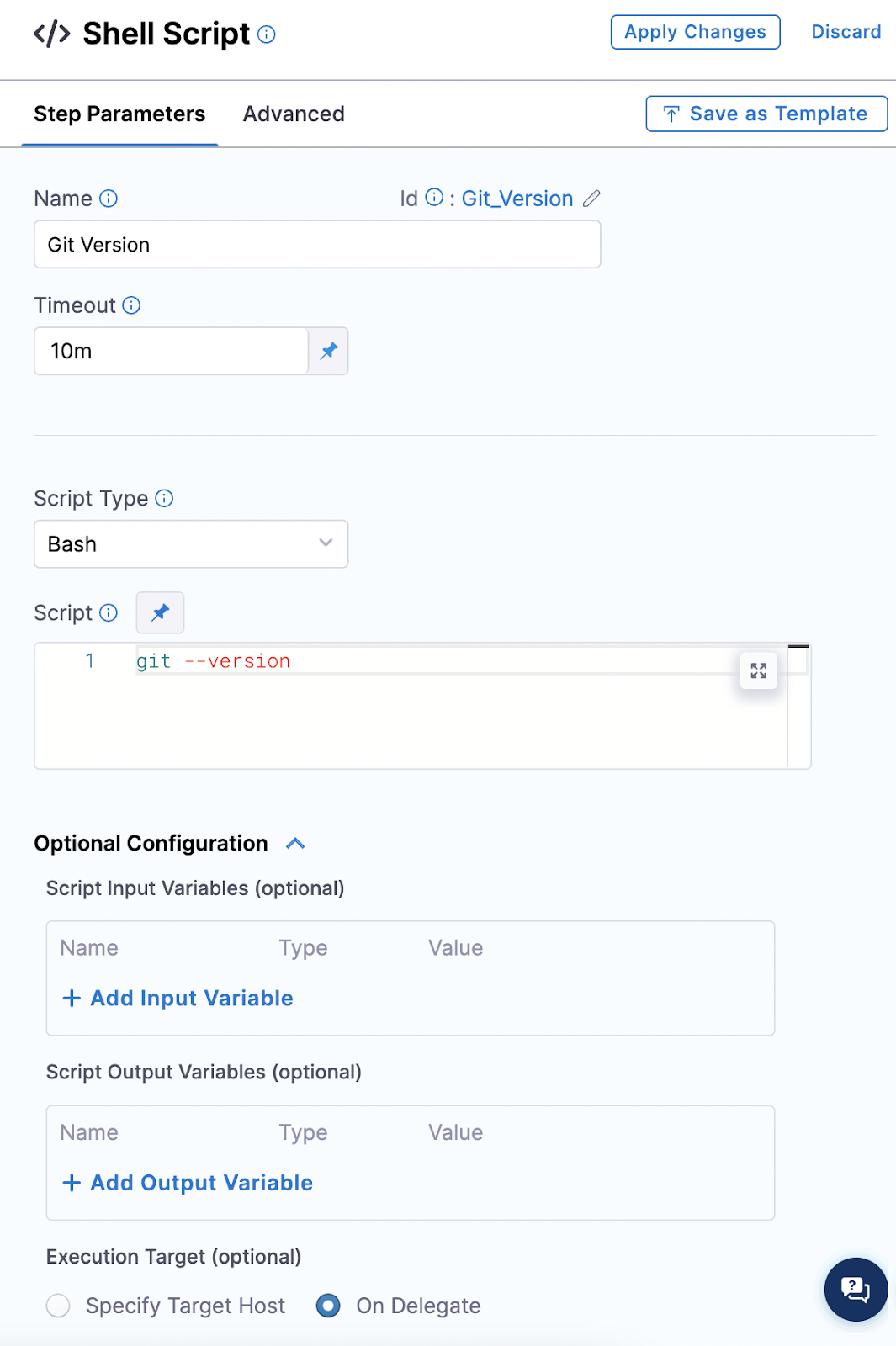
You can modify this step to test any command for the tool. For example, if you installed Helm, you could run a test to deploy a Helm chart:
helm create my-new-chart
helm install my-new-chart ./my-new-chart
helm ls -
Set the Execution Target to On Delegate.
-
On the Advanced tab, select the delegate you just modified.
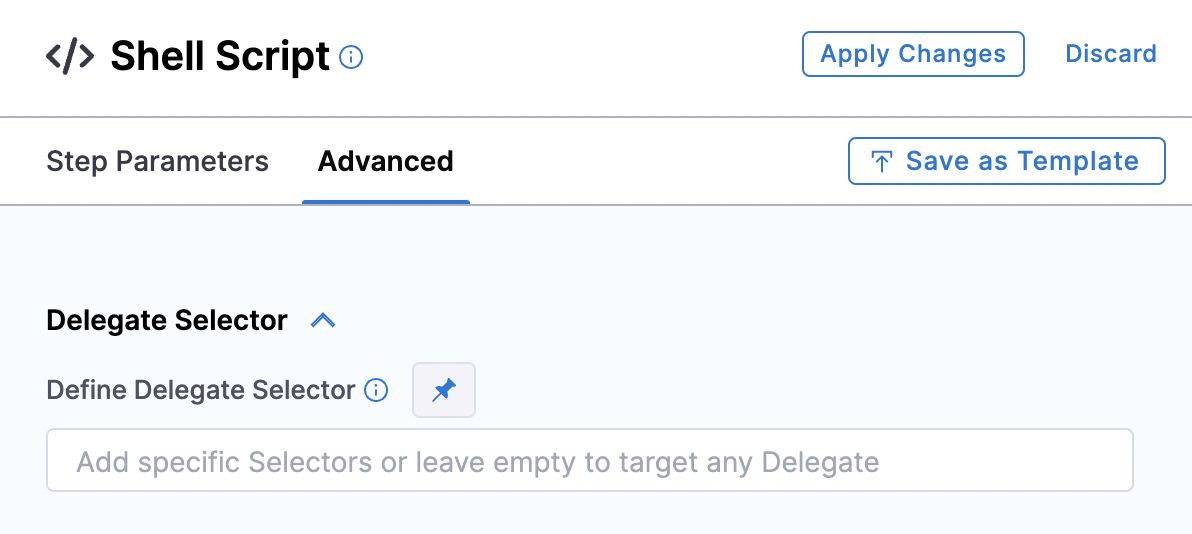
-
Save and run the pipeline. If the tool was installed on the delegate successfully, you should see the output of your script in the execution logs.
Build a custom image
This option installs the 3rd party custom binaries on a new custom delegate image that uses the Harness minimal delegate image as its base image. Below is an inline tutorial that shows you how to use this option. You can also review the tutorial directly. Go to Build custom delegate images with third-party tools.
Build a custom image
Harness Manager installs and configures delegates with the binaries that most CI/CD pipelines require. In some cases, however, a preconfigured image isn't the right fit. For example, preconfigured images can:
- Introduce the vulnerabilities of the binaries they include.
- Restrict you to the use of the included third-party tools and versions.
This document explains how you can:
- Build and host a custom delegate image that includes the tools you select.
- Use your custom delegate in CI/CD pipelines.
Delegates with an immutable image type (image tag yy.mm.xxxxx) include non-root user privileges and are compatible with OpenShift. For information on delegate types, go to Delegate image types.
About the Harness Delegate minimal image
Harness recommends that you use the Harness Delegate minimal image (yy.mm.xxxxx.minimal) when you set up the Harness Platform for production use. This image has been thoroughly scanned and is free of any high or critical vulnerabilities. Users focused on security tend to prefer this option.
However, the minimal delegate image lacks some binaries that are required for Continuous Delivery (CD) steps to function properly and remain vulnerability-free from third-party tools. Consequently, using the minimal delegate image requires you to configure your delegates and install necessary binaries. For information on delegate types, go to Delegate image types.
The Harness Delegate minimal image (yy.mm.xxxxx.minimal) is a lighter, more secure version of the default Harness Delegate image. Its main purpose is to provide an enhanced security profile for users, especially those who prioritize their systems' security. The Harness Delegate minimal images includes the following features.
-
Security Scanned: The image undergoes rigorous scanning processes to ensure that it is devoid of any high-risk or critical vulnerabilities. This makes it an optimal choice for organizations or users who have stringent security requirements. Harness aims to minimize critical/high vulnerabilities within this image. Achieving complete mitigation isn't always possible due to the continual discovery of vulnerabilities in third-party libraries/tools without immediate remediation.
-
Limited Binaries: Unlike the standard delegate, the minimal image does not include all of the default binaries. While this contributes to its lightweight nature and security, it also means that users have additional responsibilities. They must manually configure and add any necessary binaries to make their setup functional.
-
User Responsibilities: Because the minimal delegate image is devoid of the default binaries, users are in charge of tailoring it to their needs. This includes installing specific binaries essential for their CD steps. This level of control also allows users to maintain an updated environment. By installing the latest versions of necessary binaries, they can ensure that the delegate remains free from potential vulnerabilities found in outdated third-party tools.
-
Preferred by Security-Conscious Users: Due to its clean security slate, many users who prioritize system security gravitate towards the minimal delegate image. By starting with a minimal setup and adding only what is necessary, they can maintain a tighter control over the software and tools present, thus minimizing potential security risks.
Use the delegate minimal image to create a custom delegate image
Select the delegate minimal image
You can build on either of the following Harness-provided images.
| Image | Description |
|---|---|
| Harness Delegate Docker image | A publicly available Docker image providing Harness Delegate. |
| Harness Minimal Delegate Docker image | A minimal delegate image is available in Docker Hub at https://hub.docker.com/r/harness/delegate/tags. |
Use the last published yy.mm.xxxxx version of the minimal image from the Docker repository.
Build the delegate image
When you build a custom delegate image, you modify the image you select with user privileges and binaries. This section explains the build script used for the process. In this example, the script builds a custom image for deployment by Kubernetes and by Terraform.
The first lines of the script provide information about the base image and user privileges. This example uses the minimal image with delegate minor version 77029.
FROM harness/delegate:24.04.82804.minimal
USER root
The delegate container is granted root user privileges.
The first RUN block installs or updates the unzip and yum-utils tools. The --nodocs option prevents the installation of documentation on the image.
RUN microdnf update \
&& microdnf install --nodocs \
unzip \
yum-utils
The second RUN block uses the yum utility to create a configuration file for the HashiCorp repository, and then uses the microdnf package manager to install the required Terraform components:
RUN yum-config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.releases.hashicorp.com/RHEL/hashicorp.repo \
&& microdnf install -y terraform
The final RUN block retrieves the Kubernetes kubectl command-line tool that is required to manipulate clusters. The Linux chmod +x instruction makes the utility executable:
RUN mkdir /opt/harness-delegate/tools && cd /opt/harness-delegate/tools \
&& curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl> -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" && chmod +x kubectl
The ENV instruction defines the Linux $PATH environment variable that provides the location of the tools to be installed:
ENV PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/tools/:$PATH
The final instruction switches the user back to harness to ensure the custom image does not run as root:
USER harness
The complete script is as follows:
FROM harness/delegate:24.04.82804.minimal
USER root
RUN microdnf update \
&& microdnf install --nodocs \
unzip \
yum-utils
RUN yum-config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.releases.hashicorp.com/RHEL/hashicorp.repo \
&& microdnf install -y terraform
RUN mkdir /opt/harness-delegate/tools && cd /opt/harness-delegate/tools \
&& curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" && chmod +x kubectl
ENV PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/tools/:$PATH
USER harness
The following example Dockerfile adds all the tools necessary for the Harness platform that are not part of the base image to the minimal delegate. You can remove tools for features you don't use or update versions for your requirements.
Example Dockerfile with all tools
FROM harness/delegate:yy.mm.xxxxx.minimal
USER 0
ENV TARGETARCH=amd64
RUN microdnf install --nodocs git \
&& microdnf clean all \
&& rm -rf /var/cache/yum
RUN mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/kubectl/v1.24.3 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/kubectl/v1.24.3/kubectl https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/kubectl/release/v1.24.3/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/kubectl \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/helm/v2.13.1 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/helm/v2.13.1/helm https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/helm/release/v2.13.1/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/helm \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/helm/v3.1.2 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/helm/v3.1.2/helm https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/helm/release/v3.1.2/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/helm \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/helm/v3.8.0 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/helm/v3.8.0/helm https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/helm/release/v3.8.0/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/helm \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/go-template/v0.4.2 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/go-template/v0.4.2/go-template https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/go-template/release/v0.4.2/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/go-template \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/harness-pywinrm/v0.4-dev \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/harness-pywinrm/v0.4-dev/harness-pywinrm https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/harness-pywinrm/release/v0.4-dev/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/harness-pywinrm \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/chartmuseum/v0.15.0 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/chartmuseum/v0.15.0/chartmuseum https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/chartmuseum/release/v0.15.0/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/chartmuseum \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/tf-config-inspect/v1.2 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/tf-config-inspect/v1.2/terraform-config-inspect https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/terraform-config-inspect/v1.2/linux/$TARGETARCH/terraform-config-inspect \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/oc/v4.2.16 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/oc/v4.2.16/oc https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/oc/release/v4.2.16/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/oc \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/kustomize/v4.5.4 \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/kustomize/v4.5.4/kustomize https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/kustomize/release/v4.5.4/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/kustomize \
&& mkdir -m 777 -p client-tools/scm/f1024c6b \
&& curl -s -L -o client-tools/scm/f1024c6b/scm https://app.harness.io/public/shared/tools/scm/release/f1024c6b/bin/linux/$TARGETARCH/scm \
&& chmod -R 775 /opt/harness-delegate \
&& chgrp -R 0 /opt/harness-delegate \
&& chown -R 1001 /opt/harness-delegate
ENV PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/client-tools/kubectl/v1.24.3/:$PATH
ENV PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/client-tools/go-template/v0.4.2/:$PATH
ENV PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/client-tools/chartmuseum/v0.15.0/:$PATH
ENV PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/client-tools/tf-config-inspect/v1.2/:$PATH
ENV PATH=/opt/harness-delegate/client-tools/kustomize/v4.5.4/:$PATH
USER 1001
Upload the image to Docker Hub
The next step is to upload your custom image to Docker Hub. For information on working with Docker repositories, go to Manage repositories in the Docker documentation.
Modify the delegate manifest
Before you can deploy a delegate, you must:
- Update the image path to the repository location of the custom image.
- Suspend delegate auto-upgrade functionality.
Delegate auto-upgrade is not compatible with custom images.
Example manifest file
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: harness-delegate-ng
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: harness-delegate-ng-cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: custom-del-account-token
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
type: Opaque
data:
DELEGATE_TOKEN: ""
---
# If delegate needs to use a proxy, please follow instructions available in the documentation
# /docs/first-gen/firstgen-platform/account/manage-delegates/configure-delegate-proxy-settings/
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
harness.io/name: custom-del
name: custom-del
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
harness.io/name: custom-del
template:
metadata:
labels:
harness.io/name: custom-del
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
prometheus.io/port: "3460"
prometheus.io/path: "/api/metrics"
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 600
restartPolicy: Always
containers:
- image: foobar/org:custom-delegate
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: delegate
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
runAsUser: 0
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
resources:
limits:
cpu: "0.5"
memory: "2048Mi"
requests:
cpu: "0.5"
memory: "2048Mi"
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/health
port: 3460
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 2
startupProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/health
port: 3460
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 15
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: custom-del-account-token
env:
- name: JAVA_OPTS
value: "-Xms64M"
- name: ACCOUNT_ID
value:
- name: MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT
value: https://app.harness.io/gratis
- name: DEPLOY_MODE
value: KUBERNETES
- name: DELEGATE_NAME
value: custom-del
- name: DELEGATE_TYPE
value: "KUBERNETES"
- name: DELEGATE_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: INIT_SCRIPT
value: ""
- name: DELEGATE_DESCRIPTION
value: ""
- name: DELEGATE_TAGS
value: ""
- name: NEXT_GEN
value: "true"
- name: CLIENT_TOOLS_DOWNLOAD_DISABLED
value: "true"
- name: LOG_STREAMING_SERVICE_URL
value: "https://app.harness.io/gratis/log-service/"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: delegate-service
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
harness.io/name: custom-del
ports:
- port: 8080
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: upgrader-cronjob
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
rules:
- apiGroups: ["batch", "apps", "extensions"]
resources: ["cronjobs"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: custom-del-upgrader-cronjob
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: upgrader-cronjob-sa
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: upgrader-cronjob
apiGroup: ""
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: upgrader-cronjob-sa
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: custom-del-upgrader-token
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
type: Opaque
data:
UPGRADER_TOKEN: "YOUR_DELEGATE_TOKEN"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: custom-del-upgrader-config
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
data:
config.yaml: |
mode: Delegate
dryRun: false
workloadName: custom-del
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
containerName: delegate
delegateConfig:
accountId: YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID
managerHost: https://app.harness.io/gratis
---
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
labels:
harness.io/name: custom-del-upgrader-job
name: custom-del-upgrader-job
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
spec:
suspend: true
schedule: "0 */1 * * *"
concurrencyPolicy: Forbid
startingDeadlineSeconds: 20
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
serviceAccountName: upgrader-cronjob-sa
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- image: harness/upgrader:latest
name: upgrader
imagePullPolicy: Always
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: custom-del-upgrader-token
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/config
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: custom-del-upgrader-config
Upgrade the image path
Open the delegate manifest file and locate the container spec (spec.containers). Change the image path to reflect the repository location of your uploaded image as shown in the following YAML.
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 600
restartPolicy: Always
containers:
- image: example/org:custom-delegate
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: delegate
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
runAsUser: 0
For purposes of this example, the image was uploaded to example/org:custom-delegate.
Suspend delegate auto-upgrade
Before you deploy a custom delegate, you must suspend its auto-upgrade functionality. This step prevents your image from being automatically upgraded and the installed binaries removed.
To suspend auto-upgrade, in the delegate manifest, locate the CronJob resource. In the resource spec, set the suspend field to true as shown in the following YAML:
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
labels:
harness.io/name: custom-del-upgrader-job
name: custom-del-upgrader-job
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
spec:
suspend: true
schedule: "0 */1 * * *"
concurrencyPolicy: Forbid
startingDeadlineSeconds: 20
Deploy the delegate
You can deploy the delegate from Harness Manager or by applying the modified delegate manifest file to your cluster.
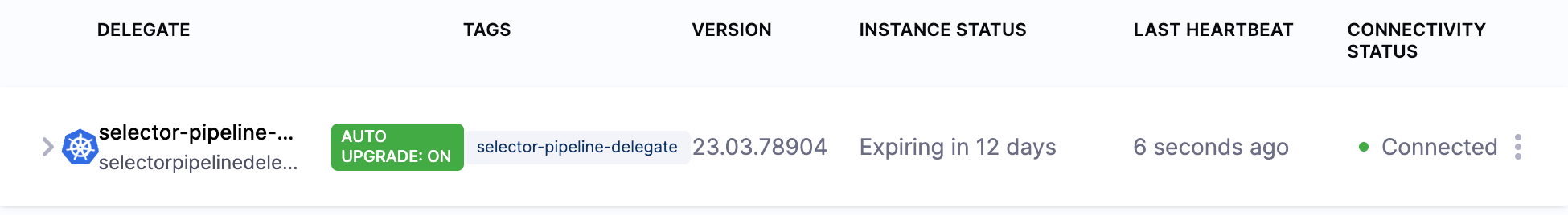
You can confirm the successful deployment and registration of the delegate in Harness Manager. Check the delegate information to ensure that auto-upgrade is not enabled.
Use your custom delegate image in pipelines
You can use your registered delegate to run Kubernetes and Terraform pipelines. It is a good idea to run a pipeline to validate the delegate image. Harness steps in your pipelines use the installed tooling on the delegate to perform builds or deployments.
For information about creating a Kubernetes pipeline, go to Kubernetes deployment tutorial.
For information about creating a Terraform Plan, go to Provision with the Terraform Apply Step.
Configure options
Network proxy
For network proxy details, go to Configure delegate proxy settings.
CI-specific variables
Delegate variables specific to CI are described where necessary, such as in Set up a local runner build infrastructure and Set up VM build infrastructures.
Custom certificates
For custom certificates, go to Install delegates with custom certificates.
Group names
The legacy delegate used DELEGATE_GROUP_NAME for group names. This environment is not valid in NextGen. Use DELEGATE_NAME for group names.
Additional installation approaches
Install Docker delegate to Amazon ECS Fargate
You can install the Docker delegate into Amazon ECS Fargate. For more information, go to Deploy a Docker delegate to Amazon ECS or AWS Fargate.
Install a legacy Kubernetes delegate
This is an End of Support (EOS) notice for the Delegate-Legacy image type. This image type reached End of Support (EOS) as of January 31, 2024.
End of Support means the following:
- Harness Support will no longer accept support requests for the Delegate-Legacy image type in both Harness FirstGen and Harness NextGen (including Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition (SMP)).
- Security fixes will still be addressed.
- Product defects will not be addressed.
The legacy Kubernetes delegate, denoted latest container image tag, is used primarily in Harness FirstGen had the auto-upgrade setting ON by default and did not have the flexibility to turn OFF this setting if needed. This type of delegate is now deprecated for new Harness accounts. For more information, go to Install a legacy Kubernetes delegate.
Install Docker delegate using Podman
You can install the Docker delegate using Podman by adding Podman commands to your Dockerfile.
To install the Docker delegate using Podman, do the following:
-
In Harness, select Deployments, then select your project.
-
Under Project Setup, select Delegates.
-
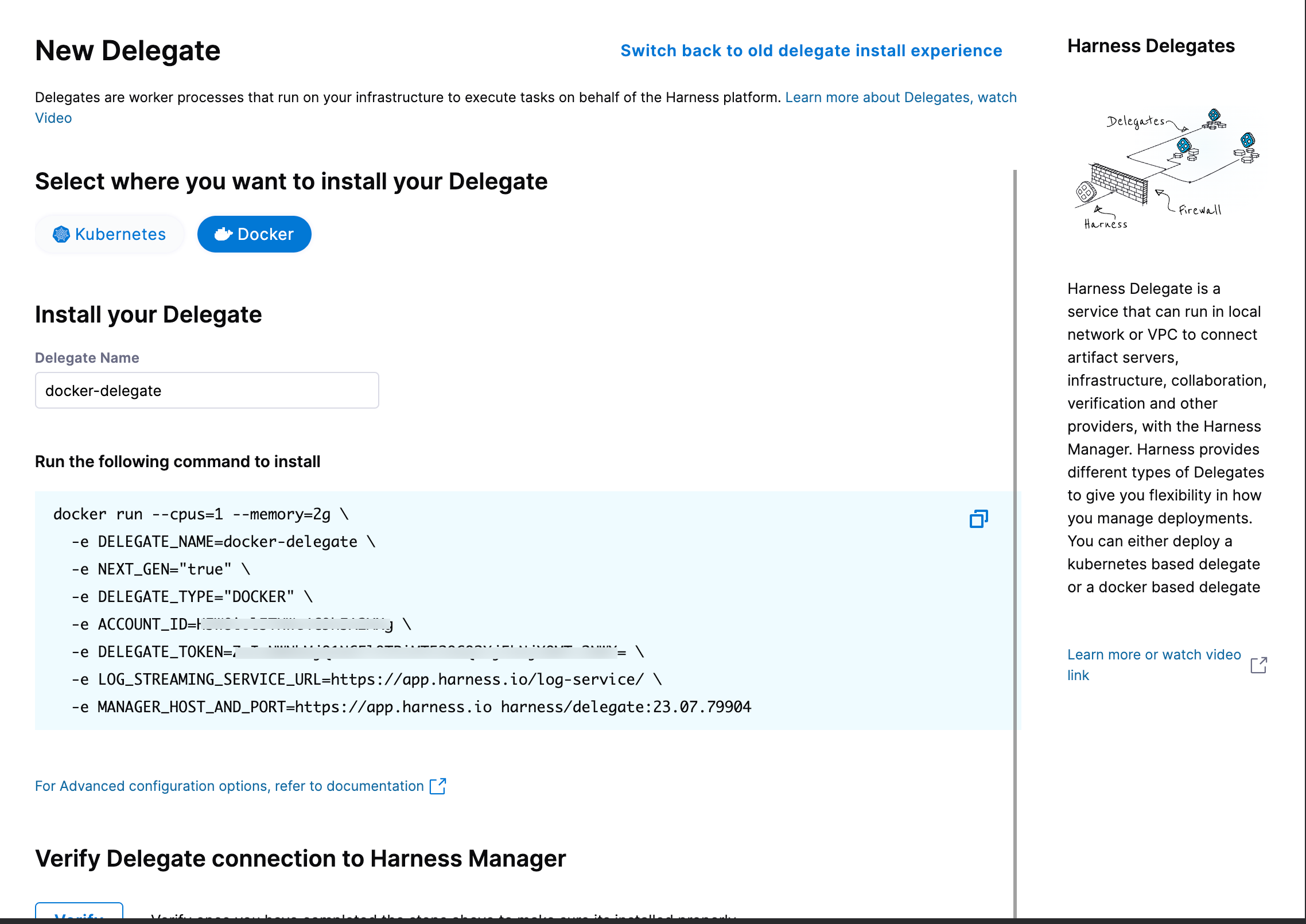
Select Install a Delegate to open the New Delegate dialog.
-
Under Select where you want to install your Delegate, select Docker.
-
Copy the Docker installation command.
-
Paste the Docker installation command from the UI in your CLI, and replace the
docker runcommand with thepodman runcommand below.podman run --restart=always --hostname="$(hostname -f)"
-e DELEGATE_NAME=docker-delegate \
-e NEXT_GEN="true" \
-e DELEGATE_TYPE="DOCKER" \
-e ACCOUNT_ID=<ACCOUNT_ID_COPIED_FROM_THE_UI_COMMAND> \
-e DELEGATE_TOKEN=<DELEGATE_TOKEN_COPIED_FROM_THE_UI_COMMAND>= \
-e LOG_STREAMING_SERVICE_URL=https://app.harness.io/log-service/ \
-e MANAGER_HOST_AND_PORT=https://app.harness.io harness/delegate:yy.mm.verno -
Run the command.