ECS container HTTP latency
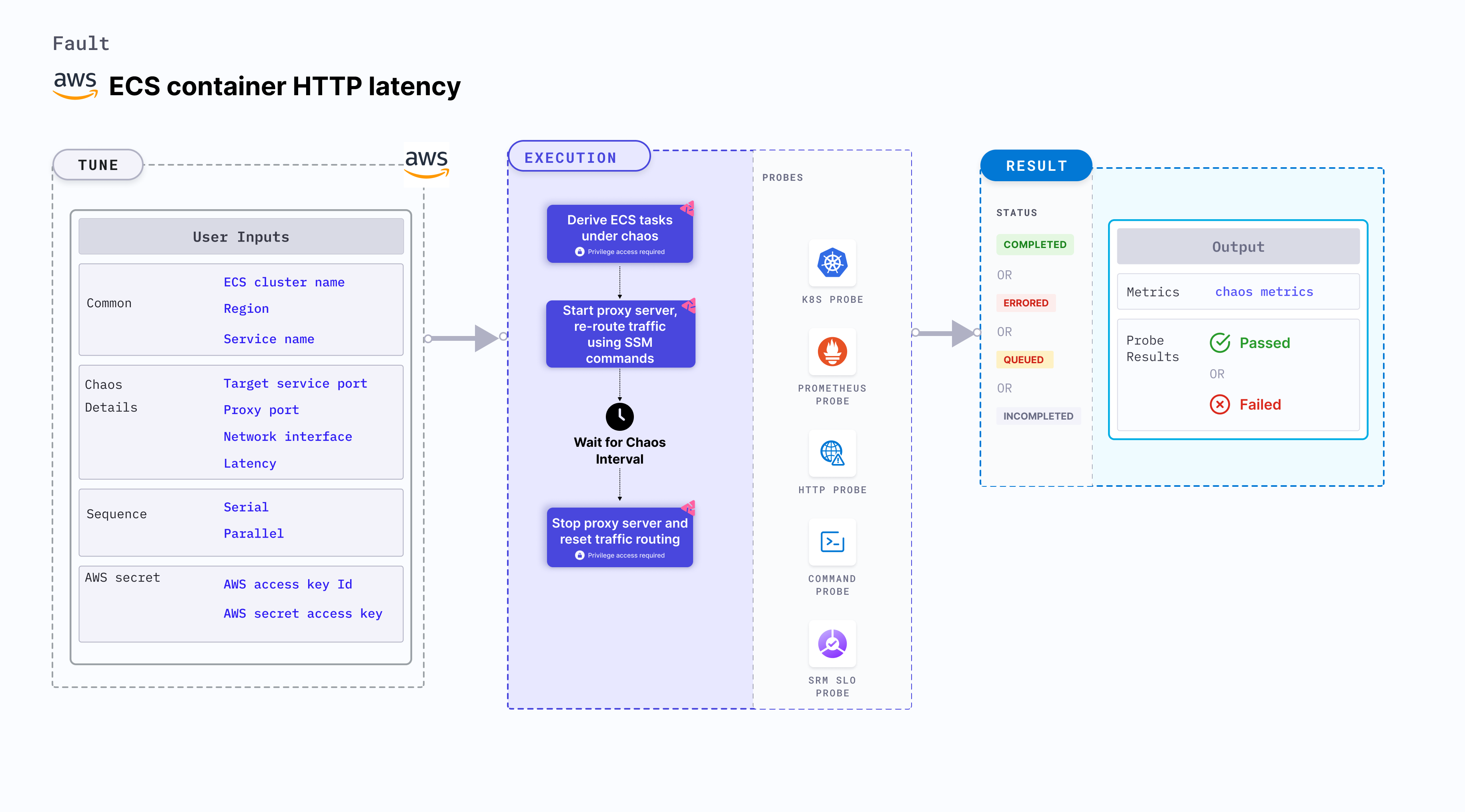
ECS container HTTP latency induces HTTP chaos on containers running in an Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service) task. This fault introduces latency in the HTTP responses of containers of a specific service using a proxy server, simulating delays in network connectivity or slow responses from the dependent services. This experiment induces chaos within a container and depends on an EC2 instance. Typically, these are prefixed with "ECS container" and involve direct interaction with the EC2 instances hosting the ECS containers.
Use cases
ECS container HTTP latency:
- Modifies the HTTP responses of containers in a specified ECS service by starting a proxy server and redirecting traffic through the proxy server.
- Simulates scenarios where containers experience delays in network connectivity or slow responses from dependent services, which may impact the behavior of your application.
- Validates the behavior of your application and infrastructure during simulated HTTP latency, such as:
- Testing how your application handles delays in network connectivity from containers to dependent services.
- Verifying the resilience of your system when containers experience slow responses from dependent services.
- Evaluating the impact of HTTP latency on the performance and availability of your application.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes >= 1.17
- ECS container metadata is enabled (disabled by default). To enable it, go to container metadata. If your task is currently running, restart it to get the metadata directory.
- ECS cluster running with the desired tasks and containers and familiarity with ECS service update and deployment concepts.
- Access to the ECS cluster instances with the necessary permissions to update the start and stop timeouts for containers. Go to systems manager documentation.
- Backup and recovery mechanisms in place to handle potential failures during the testing process.
- You and the ECS cluster instances have a role with the required AWS access to perform the SSM and ECS operations.
- Kubernetes secret with AWS Access Key ID and secret access key credentials in the
CHAOS_NAMESPACE. Below is the sample secret file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: cloud-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
cloud_config.yml: |-
# Add the cloud AWS credentials respectively
[default]
aws_access_key_id = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
aws_secret_access_key = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
HCE recommends that you use the same secret name, that is, cloud-secret. Otherwise, you will need to update the AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE environment variable in the fault template with the new secret name and you won't be able to use the default health check probes.
Below is an example AWS policy to execute the fault.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ssm:GetDocument",
"ssm:DescribeDocument",
"ssm:GetParameter",
"ssm:GetParameters",
"ssm:SendCommand",
"ssm:CancelCommand",
"ssm:CreateDocument",
"ssm:DeleteDocument",
"ssm:GetCommandInvocation",
"ssm:UpdateInstanceInformation",
"ssm:DescribeInstanceInformation"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2messages:AcknowledgeMessage",
"ec2messages:DeleteMessage",
"ec2messages:FailMessage",
"ec2messages:GetEndpoint",
"ec2messages:GetMessages",
"ec2messages:SendReply"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2:DescribeInstanceStatus",
"ec2:DescribeInstances"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
- You can pass the VM credentials as secrets or as a
ChaosEngineenvironment variable. - The ECS task container should be in a healthy state before and after introducing chaos.
- Refer to the superset permission or policy to execute all AWS faults.
- Refer to the common attributes to tune the common tunables for all the faults.
- Refer to AWS named rrofile for chaos to use a different profile for AWS faults.
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| REGION | The AWS region ID where the ECS container has been created. | For example, us-east-1. |
| LATENCY | Provide latency to be added to request in milliseconds. | For example, 2000 ms. For more information, go to latency. |
| TARGET_SERVICE_PORT | Port of the service to target | Defaults to port 80. For more information, go to target service port. |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration that you specify, through which chaos is injected into the target resource (in seconds). | Default: 30 s. For more information, go to duration of the chaos. |
| CHAOS_INTERVAL | Time interval between two successive instance terminations (in seconds). | Default: 30 s. For more information, go to chaos interval. |
| CLUSTER_NAME | Name of the target ECS cluster | Single name supported For example, demo-cluster. For more information, go to cluster name. |
| TASK_REPLICA_AFFECTED_PERC | Percentage of total tasks that are targeted. | Default: 100. For more information, go to ECS task replica affected percentage. |
| SERVICE_NAME | Target ECS service name. | For example, app-svc. For more information, go to ECS service name. |
| TASK_REPLICA_ID | Comma-separated target task replica IDs. | SERVICE_NAME and TASK_REPLICA_ID are mutually exclusive. If both the values are provided, SERVICE_NAME takes precedence. For more information, go to ECS task replica ID. |
| AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE | Provide the path for AWS secret credentials. | Defaults to /tmp/cloud_config.yml. |
| SEQUENCE | It defines a sequence of chaos execution for multiple instances. | Default: parallel. Supports serial and parallel. For more information, go to sequence of chaos execution. |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injection of chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30 s. For more information, go to ramp time. |
| INSTALL_DEPENDENCY | Specify the dependencies to be installed to run the network chaos. If the dependency exists, it can be turned off. | If the dependency already exists, you can turn it off. Defaults to True. |
| PROXY_PORT | Port where the proxy listens to requests. | Defaults to 20000. For more information, go to proxy port. |
| NETWORK_INTERFACE | Network interface used for the proxy. | Default: eth0. For more information, go to network interface. |
Target service port
Service port that is targeted. Tune it by using the TARGET_SERVICE_PORT environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the port of the targeted service
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: aws-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-container-http-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Proxy port
Port where the proxy server listens to the requests. Tune it by using the PROXY_PORT environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# provide the port for proxy server
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-container-http-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the port for proxy server
- name: PROXY_PORT
value: '8080'
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Network latency
Delay added to the HTTP request. Tune it by using the LATENCY environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the latency value
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-container-http-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the latency value
- name: LATENCY
value: '2000'
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Network interface
Network interface used for the proxy. Tune it by using the NETWORK_INTERFACE environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the network interface for proxy
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-container-http-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the network interface for proxy
- name: NETWORK_INTERFACE
value: "eth0"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: '80'
Agent stop
Target agent that is stopped for a specific duration. Tune it by using the CLUSTER_NAME environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# stops the agent of an ECS cluster
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-agent-stop
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the name of ECS cluster
- name: CLUSTER_NAME
value: 'demo'
- name: REGION
value: 'us-east-2'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
VALUE: '60'
ECS task replica affected percentage
Number of tasks to target (in percentage). Tune it by using the TASK_REPLICA_AFFECTED_PERC environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# stop the tasks of an ECS cluster
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-task-stop
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the name of ECS cluster
- name: CLUSTER_NAME
value: 'demo'
- name: SERVICE_NAME
vale: 'test-svc'
- name: TASK_REPLICA_AFFECTED_PERC
vale: '100'
- name: REGION
value: 'us-east-1'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
VALUE: '60'
ECS task replica IDs
Task replicas that have a specific ID which are to be stoppee. Tune it by using the TASK_REPLICA_ID environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# stop the tasks of an ECS cluster
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-task-stop
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the name of ECS cluster
- name: CLUSTER_NAME
value: 'demo'
- name: TASK_REPLICA_ID
vale: '1b751cf956e34e54b9d83b6a5c067f60,20d5041c044941dfb2126f1722d10558'
- name: REGION
value: 'us-east-1'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
VALUE: '60'
ECS service name
Service name whose tasks are stopped. Tune it by using the SERVICE_NAME environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# stop the tasks of an ECS cluster
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-task-stop
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the name of ECS cluster
- name: CLUSTER_NAME
value: 'demo'
- name: SERVICE_NAME
vale: 'test-svc'
- name: REGION
value: 'us-east-1'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
VALUE: '60'