Pod HTTP status code
Pod HTTP status code is a Kubernetes pod-level fault that injects chaos inside the pod by modifying the status code of the response from the application server to the desired status code provided by the user. This is achieved by starting the proxy server and redirecting the traffic through the proxy server.
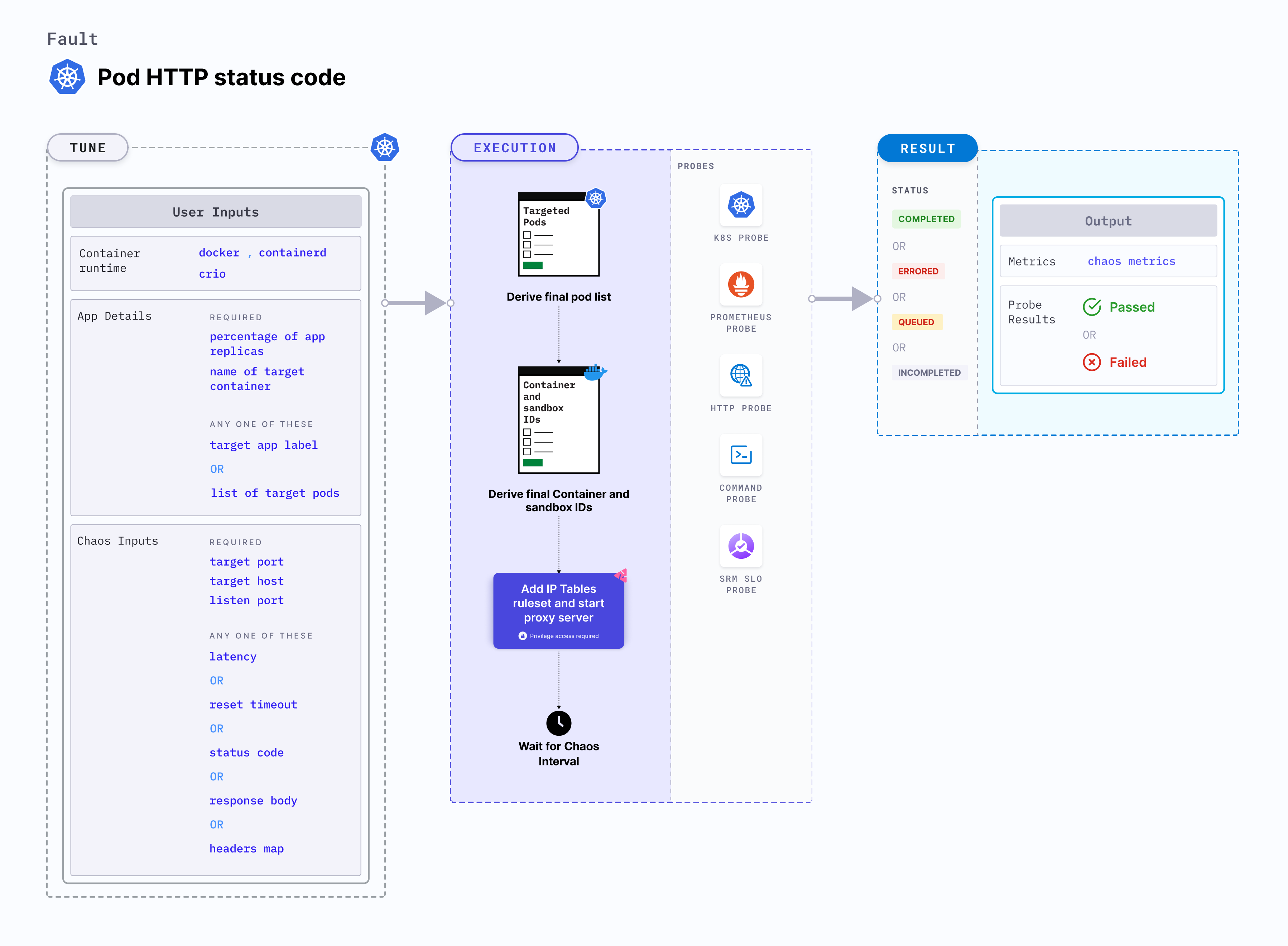
Use cases
Pod HTTP status code:
- Tests the application's resilience to error code HTTP responses from the provided application server.
- Simulates unavailability of specific API services (503, 404).
- Simulates unavailability of specific APIs for (or from) a given microservice.
- Simulates unauthorized requests for third party services (401 or 403), and API malfunction, that is internal server error (50x).
Permissions required
Below is a sample Kubernetes role that defines the permissions required to execute the fault.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: hce
name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
definition:
scope: Cluster # Supports "Namespaced" mode too
permissions:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "deletecollection", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "get", "list", "patch", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/log"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["deployments, statefulsets"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["replicasets, daemonsets"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["chaosEngines", "chaosExperiments", "chaosResults"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "deletecollection"]
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes > 1.16
- The application pods should be in the running state before and after injecting chaos.
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TARGET_SERVICE_PORT | Port of the service to target, which refers to container that runs at pod-level. | Default: port 80. For more information, go to target service port |
| NODE_LABEL | Node label used to filter the target node if TARGET_NODE environment variable is not set. | It is mutually exclusive with the TARGET_NODE environment variable. If both are provided, the fault uses TARGET_NODE. For more information, go to node label. |
| STATUS_CODE | Modified status code for the HTTP response. Multiple values can be provided as a comma-separated list. A random value from the provided list will be selected. Supported values include [200, 201, 202, 204, 300, 301, 302, 304, 307, 400, 401, 403, 404, 500, 501, 502, 503, 504]. | If no value is provided, a random value is selected from the list of supported values. Defaults to random status code. For more information, go to status code |
| MODIFY_RESPONSE_BODY | Specifies whether to modify the body according to the status code provided. | If true, the body is replaced by a default template for the status code. Defaults to true. For more information, go to modify response body |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| RESPONSE_BODY | String body to overwrite the HTTP response body. This is used only if MODIFY_RESPONSE_BODY is set to true. If no value is provided, response will be an empty body. | Default: empty body. For more information, go to response body |
| CONTENT_ENCODING | Encoding type to compress/encode the response body | Accepted values are: gzip, deflate, br, identity. Defaults to none (no encoding). For more information, go to content encoding |
| CONTENT_TYPE | Content type of the response body | Default: text or plain. For more information, go to content type |
| PROXY_PORT | Port where the proxy will be listening for requests | Default: 20000. For more information, go to proxy port |
| NETWORK_INTERFACE | Network interface to be used for the proxy | Default: eth0. For more information, go to network interface |
| TOXICITY | Percentage of HTTP requests to be affected. | Default: 100. For more information, go to toxicity |
| CONTAINER_RUNTIME | Container runtime interface for the cluster. | Default: containerd. Supports docker, containerd and crio. For more information, go to container runtime |
| SOCKET_PATH | Path of the containerd/crio/docker socket file | Default: /run/containerd/containerd.sock. For more information, go to socket path |
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration for which to insert chaos (in seconds). | Default: 60 s. For more information, go to duration of the chaos |
| TARGET_PODS | Comma-separated list of application pod names subject to pod HTTP status code. | If not provided, the fault selects target pods randomly based on provided appLabels. For more information, go to target specific pods |
| PODS_AFFECTED_PERC | Percentage of total pods to target. Provide numeric values. | Default: 0 (corresponds to 1 replica). For more information, go to pod affected percentage |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30 s. For more information, go to ramp time |
| SEQUENCE | Sequence of chaos execution for multiple target pods. | Default: parallel. Supports serial and parallel. For more information, go to sequence of chaos execution |
Target service port
Port of the target service. This is the port where the application runs at the pod-level. For example, if the application pod is running the service at port 8080 and you create a service exposing this service at port 80, the target service port should be 8080.
Tune it by using the TARGET_SERVICE_PORT environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the port of the targeted service
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
# modified status code for the http response
- name: STATUS_CODE
value: "500"
Proxy port
Port where the proxy server listens for requests. Tune it by using the PROXY_PORT environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the port for proxy server
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the port for proxy server
- name: PROXY_PORT
value: "8080"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
# modified status code for the http response
- name: STATUS_CODE
value: "500"
Status code
Status code to be modified for the HTTP response. Tune it by using the STATUS_CODE environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## modified status code for the http response
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
components:
env:
# modified status code for the http response
# if no value is provided, a random status code from the supported code list will selected
# if multiple comma separated values are provided, then a random value from the provided list will be selected
# if an invalid status code is provided, the fault will fail
# supported status code list: [200, 201, 202, 204, 300, 301, 302, 304, 307, 400, 401, 403, 404, 500, 501, 502, 503, 504]
- name: STATUS_CODE
value: "500"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Modify response body
Specifies whether or not to modify the response body with a pre-defined template to match the status code value of the HTTP response. Tune it by using the MODIFY_RESPONSE_BODY environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## whether to modify the body as per the status code provided
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
components:
env:
# whether to modify the body as per the status code provided
- name: "MODIFY_RESPONSE_BODY"
value: "true"
# modified status code for the http response
- name: STATUS_CODE
value: "500"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Toxicity
Percentage of the total number of HTTP requests to be affected. Tune it by using the TOXICITY environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the toxicity
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
components:
env:
# toxicity is the probability of the request to be affected
# provide the percentage value in the range of 0-100
# 0 means no request will be affected and 100 means all request will be affected
- name: TOXICITY
value: "100"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Response body
String body used to overwrite the HTTP response body. Tune it by using the RESPONSE_BODY environment variable.
The MODIFY_RESPONSE_BODY environment variable should be set to true to enable this feature.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the response body value
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the body string to overwrite the response body. This will be used only if MODIFY_RESPONSE_BODY is set to true
- name: RESPONSE_BODY
value: "<h1>Hello World</h1>"
# whether to modify the body as per the status code provided
- name: "MODIFY_RESPONSE_BODY"
value: "true"
# modified status code for the http response
- name: STATUS_CODE
value: "500"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Content encoding and content type
Content encoding and content type of the response body. Tune it by using the CONTENT_ENCODING and CONTENT_TYPE environment variables, respectively.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## whether to modify the body as per the status code provided
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the encoding type for the response body
# currently supported value are gzip, deflate
# if empty no encoding will be applied
- name: CONTENT_ENCODING
value: "gzip"
# provide the content type for the response body
- name: CONTENT_TYPE
value: "text/html"
# whether to modify the body as per the status code provided
- name: "MODIFY_RESPONSE_BODY"
value: "true"
# modified status code for the http response
- name: STATUS_CODE
value: "500"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
Network interface
Network interface used for the proxy. Tune it by using the NETWORK_INTERFACE environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the network interface for proxy
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the network interface for proxy
- name: NETWORK_INTERFACE
value: "eth0"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
# modified status code for the http response
- name: STATUS_CODE
value: "500"
Container runtime and socket path
The CONTAINER_RUNTIME and SOCKET_PATH environment variables to set the container runtime and socket file path, respectively.
CONTAINER_RUNTIME: It supportsdocker,containerd, andcrioruntimes. The default value iscontainerd.SOCKET_PATH: It contains path of containerd socket file by default(/run/containerd/containerd.sock). Fordocker, specify path as/var/run/docker.sock. Forcrio, specify path as/var/run/crio/crio.sock.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
## provide the container runtime and socket file path
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-http-status-code
spec:
components:
env:
# runtime for the container
# supports docker, containerd, crio
- name: CONTAINER_RUNTIME
value: "containerd"
# path of the socket file
- name: SOCKET_PATH
value: "/run/containerd/containerd.sock"
# provide the port of the targeted service
- name: TARGET_SERVICE_PORT
value: "80"
# modified status code for the http response
- name: STATUS_CODE
value: "500"