Set up disaster recovery
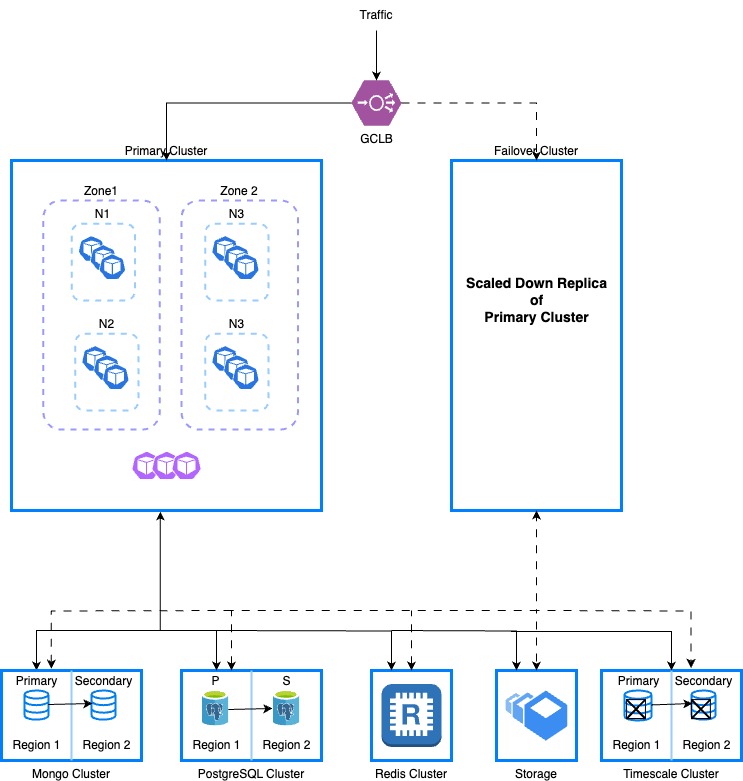
This topic explains how to set up a disaster recovery (DR) cluster with external data storage and covers best practices for DR setup in Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition.
Harness recommends that you create a multi-node cluster spread across different availability zones of a data center for better node failure tolerance.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are needed.
Each provisioned cluster should have:
- Enough resources allocated for both a primary & a DR cluster to support the installation of Harness Helm charts.
- Access to persistent storage.
External data storage must support:
- Replication of data.
- Primary database must be reachable by both the primary and a DR cluster.
- SSL support between primary and secondary database nodes.
Set up an external database
- MongoDB
- Postgres
- Redis
- TimescaleDB
To set up an external MongoDB, do the following:
-
Deploy a replica set. For more information, go to Deploy a Replica Set in the MongoDB documentation.
-
Get the MongoDB credentials by accessing the MongoDB Cloud → Database Access section.
-
Encode the credentials using command below.
echo -n 'YOUR_MONGODB_USERNAME' | base64
echo -n 'YOUR_MONGODB_PASSWORD' | base64 -
Create a
mongo-secret.yamlfile. -
Paste the encoded credentials in your
mongo-secret.yamlfile.apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mongo-secret
type: Opaque
data:
keyone: <YOUR_BASE64_ENCODED_USERNAME>
keytwo: <YOUR_BASE64_ENCODED_PASSWORD> -
Apply your
mongo-secret.yamlfile.kubectl apply -f mongo-secret.yaml -n <namespace> -
Add the following external MongoDB-specific changes in your override file.
global:
database:
mongo:
# -- set this to false if you want to use external mongo
installed: false
# -- provide default values if mongo.installed is set to false
# -- generates mongo uri protocol://hosts?extraArgs
protocol: mongodb+srv
hosts:
#mongo host names from atlas mongo cloud
- smp-xx-yy-0-zzz.u2poo.mongodb.net
secretName: mongo-secret
userKey: user
passwordKey: password
extraArgs: ""
platform:
access-control:
mongoSSL:
enabled: true
mongoHosts:
- smp-xx-yy-0-shard-00-00-zzz.xyz1.mongodb.net:27017
- smp-xx-yy-0-shard-00-00-zzz.xyz2.mongodb.net:27017
- smp-xx-yy-0-shard-00-00-zzz.xyz3.mongodb.net:27017
- smp-xx-yy-0-shard-00-00-zzz.xyz4.mongodb.net:27017
To set up an external Postgres database using Google CloudSQL, do the following:
-
Sign in to your Google console.
-
Select the project where you want to create your CloudSQL database.
-
Create a Postgres with CloudSQL instance.
-
Specify the following details.
a. Enter your instance name and password. Save this password to use as a secret when you deploy the SMP cluster.
b. Select Postgres version 14.
c. Select production for the deployment environment. This ensures HA/DR for Postgres.
d. Enable automated backups.
-
Select your database instance to go the Details page.
-
Select the Backup tab.
-
Configure the backup window and retention settings as per your requirements.
-
Select Save.
Set up read replica for replication
To set up read replica for replication, do the following:
-
In the navigation menu, go back to SQL.
-
Select your PostgreSQL instance.
-
Select the Replicas tab.
-
Select Create read replica.
-
Choose a different region to ensure high availability.
-
Configure other settings as required, and then select Create.
Configure failover
To configure failover, do the following:
-
After you create your replica, select it to go to its Details page.
-
Select the Replication tab.
-
Set up automatic promotion to a master instance in case the primary instance fails.
-
Select Save.
Configure cross-region replication
To configure cross-region replication, do the following:
- Repeat the steps in Set up read replica for replication, but choose another region to add another layer of redundancy.
Configure routing policies
Configure DNS or load balancer to redirect traffic automatically to the standby system in a different region in case of a disaster. Make sure the CloudSQL instance is paired with the Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition cluster using a private pairing.
Select the NAT of the Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition cluster here. This will create a VPC with the Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition cluster and allow Harness services running inside cluster to have access to CloudSQL.
Create a secret
To create a secret, do the following:
-
Get the Postgres database username and password for the Postgres cluster you set up in step 4 of Configure an external Postgres instance using Google CloudSQL.
-
Run the following command to encode the credentials.
echo -n 'YOUR_POSTGRES_USERNAME' | base64
echo -n 'YOUR_POSTGRES_PASSWORD' | base64 -
Create a
postgres-secret.yamlfile.apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: postgres-secret
type: Opaque
data:
user: <YOUR_BASE64_ENCODED_USERNAME>
password: <YOUR_BASE64_ENCODED_PASSWORD> -
Apply your
postgres-secret.yamlfile.kubectl apply -f postgres-secret.yaml -n <namespace> -
Add the following external Postgres-specific changes in your override file.
global:
database:
postgres:
## - set this to false if you want to use external postgres cluster
installed: false
## - protocol to use for connection
protocol: postgres
## - host array for external
hosts:
- postgres:5432
## - secret name containing external values
secretName: ""
## - key within secret containing username
userKey: ""
## - key within secret containing password
passwordKey: ""
## - extra arguments set to connection string
extraArgs: ""
To set up an external Redis database, do the following:
-
Set up your Google Cloud environment.
a. Sign in to the GCP Console and select or create your project.
b. Ensure you have the required quotas for Compute Engine instances and storage in your desired regions.
-
Deploy Redis Enterprise in the primary region.
a. Navigate to the GCP Marketplace and search for Redis Enterprise Cloud.
b. Follow the instructions to deploy Redis Enterprise to your primary region.
c. Access the Redis Enterprise admin console to manage and configure your cluster.
-
Deploy Redis Enterprise in the secondary region. Repeat the process in step 2 above to deploy another Redis Enterprise cluster in your secondary region.
-
Set up cross-region networking.
a. Ensure both Redis Enterprise deployments can communicate.
b. Use VPC network peering to enable communication between the VPCs of the two regions.
-
Configure your Redis database to be an active-active Conflict-Free Replicated Database (CRDB).
a. In Redis Enterprise, you can use a CRDB setup for geo-distributed DR capabilities. From the Redis Enterprise admin console in the primary region, create a new CRDB.
b. Add your primary and secondary clusters to the CRDB configuration.
c. Configure other CRDB settings per your requirements, such as conflict resolution.
-
Configure the applications to connect to the CRDB. Ensure that your applications can handle any conflicts or issues that might arise from the active-active configuration.
-
Add the following external Redis-specific changes in your override file.
global:
database:
redis:
installed: false
hosts:
- <YOUR_INTERNAL_ENDPOINT_WITH_PORT>
secretName: ""
userKey: ""
passwordKey: ""
To set up an external Timescale database, do the following:
-
Create an account at Managed Service for TimescaleDB.
-
Set up VPC peering with the cloud provider.
a. Go to VPC in Timescale cloud and create a new VPC connection. Make sure the IP CIDr range doesn't conflict with the cloud-provider's VPC range. b. Go to the cloud provider and initiate VPC peering by providing the project ID and VPC network.
-
Go to Timescale Services and create a service in the same region.
a. Select Timescale version 14. b. Set other configurations as per your requirements. c. Under Allowed IP addresses, set the IPv4 service range and Cluster Pod IPv4 range so traffic from the cluster is able to connect to TimescaleDB.
TimescaleDB cloud only supports SSL. For more information, go to Timescale security in the Timescale documentation.
-
Create two databases,
harnessandharnessti. -
Create two secrets,
tsdb-secretcontaining the username and password, andtsdb-cert, containing the certificate.apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: tsdb-secret
type: Opaque
data:
username: YOUR_USERNAME
password: YOUR_PASSWORDapiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: tsdb-cert
type: Opaque
data:
cert: <YOUR_BASE64_ENCODED_CERT> -
Add the following external Timescale-specific changes in your override file.
global:
database:
timescaledb:
installed: false
# -- provide default values if mongo.installed is set to false
hosts:
- hostname.timescale-cloud.a.com:27597
secretName: "tsdb-secret"
userKey: "username"
passwordKey: "password"
certName: "tsdb-cert"
certKey: "cert"
Set up the DR cluster
To use the Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition Helm chart with DR configuration, the following requirements must be met:
-
Set the DR variable to
truein theoverride.yamlfile before you deploy to the cluster to the DR cluster.global:
dr:
createCluster: true -
Use the command below to create the DR cluster.
helm install <releaseName> harness/ -n <namespace> -f override.yaml
Switch to the DR cluster
To ensure business continuity for any unplanned primary cluster failure, you can switch to DR cluster.
To switch to the DR cluster, do the following:
Before activating the DR cluster, ensure that you disable the ingress/load balancer to prevent concurrent writes to the datastore.
After traffic to the Harness primary cluster is cut-off, you can take it down before starting the DR cluster.
-
Run the following Helm command to uninstall.
helm uninstall <release name> -n <namespace> -
Update the following flags in the
override.yamlfile before you upgrade the DR cluster.global:
dr:
activateCluster: true
runConfigChecks: true -
Run the Helm upgrade command to connect to the DR cluster.
helm upgrade <release name> harness/ -f override.yaml -
Make sure the DR cluster is in a healthy state and all pods are running before you route traffic to it.